DataStructure_Algorithm_HandBook_PreForLeetCode
Given the root of a binary tree, return all root-to-leaf paths in any order.
A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
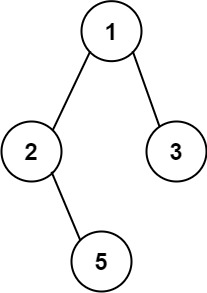
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5]
Output: ["1->2->5","1->3"]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1]
Output: ["1"]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
solution
顺序是不作要求的,就是在遍历的过程中记录当前的路径即可 因此最好是用 dfs 来做,到叶子节点就记录起来,最好是用链表来存储,因此如果用数组是需要扩容的,但是链表不需要扩容/
注意使用 stringBuilder 的时候不要直接在 path 上进行修改。 因为path 是引用数据类型,直接改的话会把其他层的也修改掉的
class Solution {
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root,new StringBuilder());
return res;
}
List<String> res = new LinkedList();
void dfs(TreeNode node, StringBuilder path){
if(node == null) return;
//复制一个新的
StringBuilder cur_path = new StringBuilder(path);
cur_path.append(node.val);
if(node.left == null && node.right == null){
res.add(cur_path.toString());
return;
}
cur_path.append("->");
dfs(node.left,cur_path);
dfs(node.right,cur_path);
}
}